
Outdoor Thermal Testing of ZERAF’s with Kinetic Cladding Variants
Miren Juaristi Gutierrez
miren.juaristigutierrez@eurac.edu
The ZERAF project tackles a major issue in the building sector: high energy consumption and the resulting greenhouse gas emissions. In the EU, buildings use about 40% of the energy and are responsible for 36% of energy-related greenhouse gas emissions. This project aims to change how buildings manage energy by proposing a new building façades technology, as facades are key to reducing energy use while keeping people comfortable.
Mainstream approaches to develop energy efficient opaque facades consists of increasing their insulation level to prevent energy loss, which helps in winter but can cause overheating in summer, especially with climate change. ZERAF addresses this by acting as both an insulator and a dissipater, adapting to the environment and user needs. This is why ZERAF technology is revolutionary: it intelligently controls heat transfer, significantly reducing the energy needed for heating and cooling buildings. Imagine the temperature difference you feel when wearing a white shirt versus a black one in the sun. This shows how ZERAF controls heat gains by radiation. For conduction, think about the difference between wearing a light t-shirt and a thick pullover. For convection, compare how sweat evaporates when wearing a technical sports t-shirt versus a regular cotton one. Essentially, ZERAF changes the “clothes” of the building to control heat exchange through radiation, conduction, and convection, based on the weather conditions, considering the heat gains in the interior of the buildings and users’ comfort expectations. ZERAF can adapt its behavior to either prevent heat loss or promote heat exchanges.
What makes ZERAF unique from other adaptive opaque façade concepts is also its innovative use of materials that simplify the technology while enhancing its adaptive capabilities. ZERAF uses bio-polyurethane and shape memory alloys to streamline the dynamic components needed for a façade adapts. Bio-polyurethane provides thermal insulation without relying on petrol-based materials, reducing the embodied carbon of the façade. Shape memory alloys simplify the dynamic components, allowing the façade to adapt efficiently to changing conditions. This combination of materials and adaptive configurations makes ZERAF a standout solution in the market.
In summary, ZERAF aims to cut down the energy demand of buildings while keeping the carbon footprint as low as possible. By harnessing environmental resources and controlling heat flows in building façades, ZERAF is set to revolutionize energy efficiency in the construction industry. Funded by the EIC Pathfinder program, this high-risk, high-reward research project is on a mission to validate its groundbreaking concept.
Stay tuned and get ready to see how ZERAF is transforming the future of building energy efficiency!


Outdoor Thermal Testing of ZERAF’s with Kinetic Cladding Variants

Interdisciplinary research: research activities and the role of different team members

Podcast episode about adaptive facade technologies
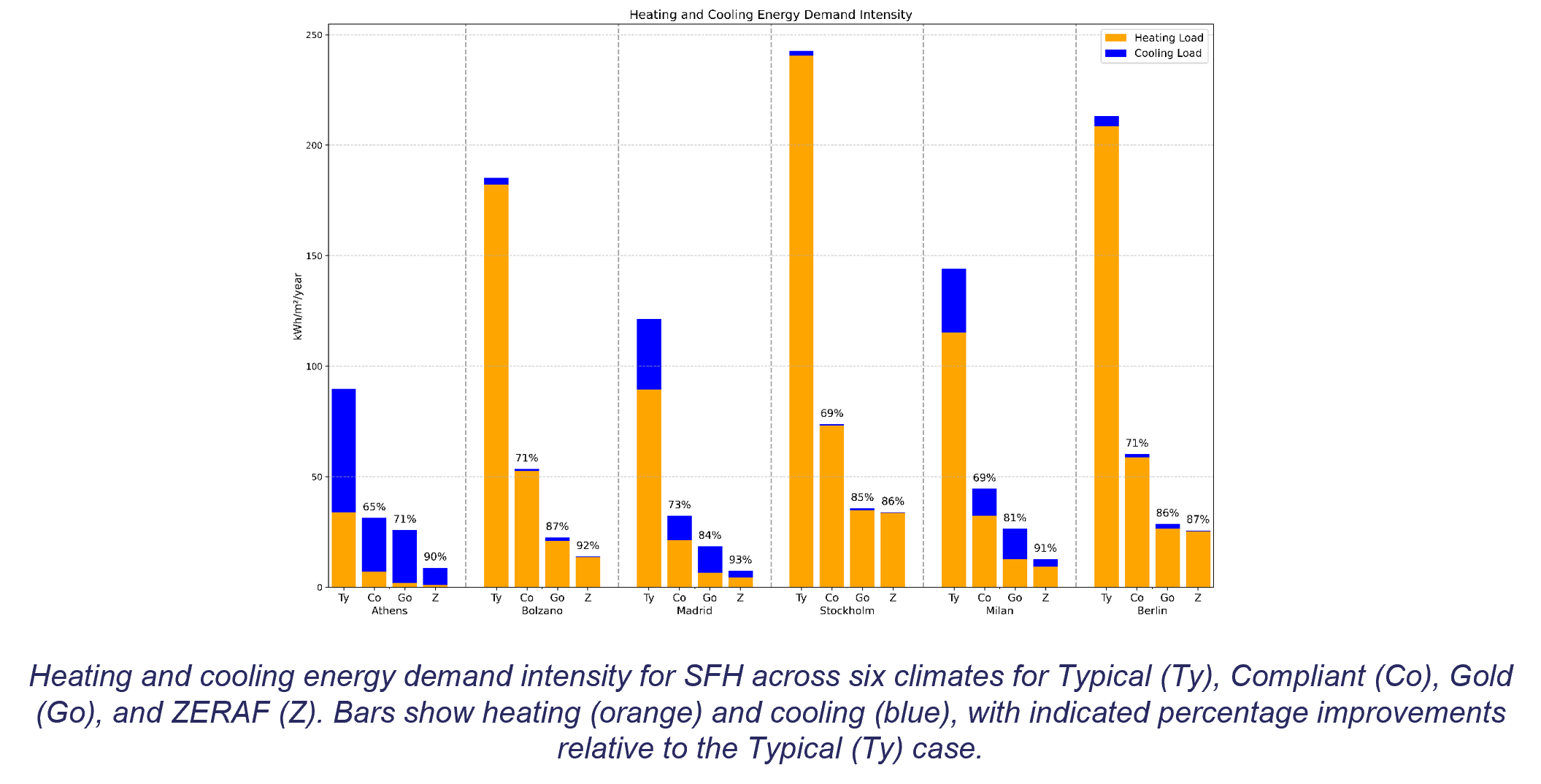
Preliminary assessment of ZERAF’s impact on operational energy use in buildings
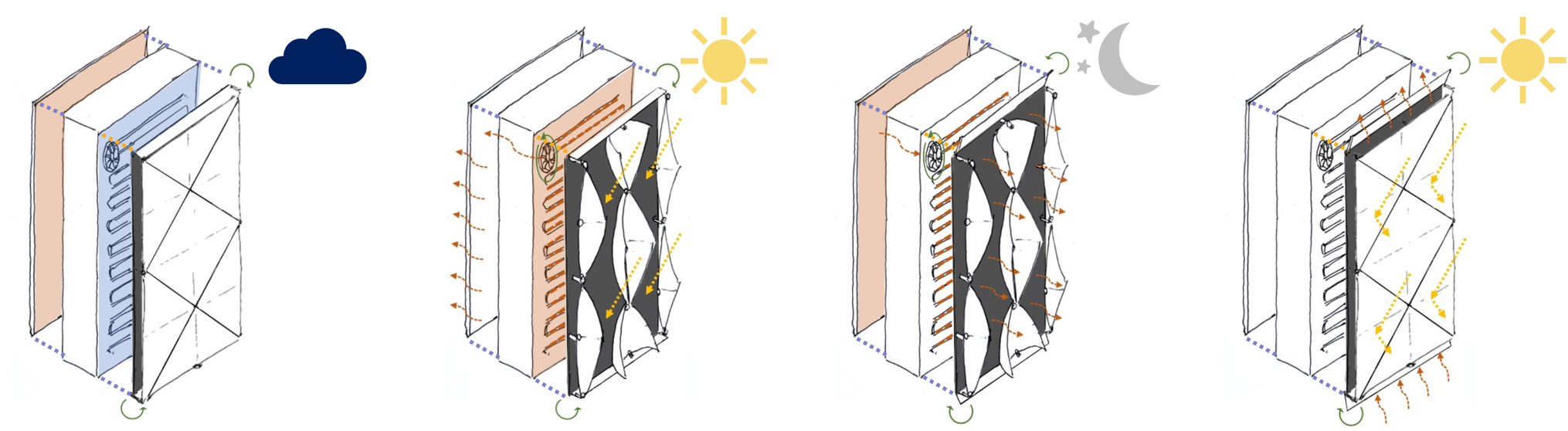
Understanding ZERAF Façade Technology: Technical Insights and Possible Variations

Project meeting of ZERAF at Ingpuls Smart Shadings

Summary & results of 2023

Technical meeting of ZERAF Project at INDRESMAT’s pilot plan

Enhancing Building Energy Performance with Intelligent Opaque Facades

Kick-off meeting of ZERAF Project in Bolzano